Dermatomyositis Complications and Related Conditions: A Complete Understanding
The rare inflammatory illness known as dermatomyositis can damage skin and muscles. It causes recognizable skin rashes and muscular weakness. With time, major problems may develop, compromising important organs. Symptoms could get worse, and quality of life might suffer without therapy. Usually, the illness causes heart problems, lung diseases, and trouble swallowing. Calcinosis, in which calcium accumulates in soft tissues, is experienced by some patients.
The weakening immune system raises one's susceptibility to illnesses. A few persons get cancer from ongoing inflammation. Early intervention depends on an awareness of possible consequences. It enhances long-term health results and helps to avoid major damage. Medications and lifestyle changes help symptoms be lessened. Patients should see doctors regularly and follow their instructions.
Lung Complications in Dermatomyositis:
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), a disorder whereby lung tissue becomes scarred, can be brought on by dermatomyositis. That lowers blood's oxygen content and makes breathing harder. Among the symptoms are constant dry coughing, dyspnea, and tiredness. Left untreated, inflammation in lung tissues might get severe. Severe cases over time could cause respiratory failure. Effectful management of ILD depends on early identification. Imaging scans and pulmonary function testing help doctors find lung involvement.
To lower inflammation, treatment consists of immunosuppressive medications and corticosteroids. Sometimes, breathing has to be improved with oxygen treatment. Patients who undergo pulmonary rehabilitation find their lungs strengthened. Reducing air pollution and smoking helps to stop more damage. Constant observation guarantees that lung problems do not get worse. Patients should promptly tell their doctor about the trouble they have breathing. Maintaining lung health not only enhances the general quality of life but also helps to avoid major issues.
Heart Problems Associated with Dermatomyositis:
In people with dermatomyositis, heart problems are rather frequent. Myocarditis, inflammation of the heart muscles, can result from the illness. This results in irregular heartbeats, dyspnea, and sore chest. Untreated myocarditis can cause heart failure. Affected blood arteries might raise the risk of coronary heart disease. Those with dermatomyositis are more prone to have heart arrhythmias and excessive blood pressure. Regular cardiac checks—including echocardiograms and ECGs—help find early issues.
Doctors mediate cardiac problems with medicines. Anticoagulants and beta-blockers may be advised. Lifestyle modifications include a good diet and moderate exercise to help cardiac performance. Patients ought to avoid too much stress since it aggravates cardiac diseases. Early identification of heart diseases guarantees improved treatment results. Monitoring symptoms and getting quick medical assistance help to avoid major problems. Good cardiovascular treatment lowers the chance of life-threatening problems.
Swallowing Difficulties and Digestive Problems
Many patients with dermatomyositis have dysphagia—difficulty swallowing. That results from esophageal and throat muscle weakness. Aspiration pneumonia, which can be fatal, and choking are more likely with dysphagia. A few patients also get acid reflux, which causes discomfort and heartburn. When swallowing problems continue, malnutrition and poor digestion become issues. To build throat muscles, a speech therapist can advise swallowing activities.
Changes in diet can help lower problems. Thicken liquids and soft foods help avoid choking. In extreme circumstances, appropriate nutrition may depend on a feeding tube. Patients should avoid hot foods and eat small, frequent meals. Common GI problems include constipation and bloating. Muscle weakness causes uncomfortable digestion. A fiber-rich diet and enough water help keep gut health intact. Patients should tell their doctor about any ongoing stomach issues.
Skin Manifestations and Long-Term Effects
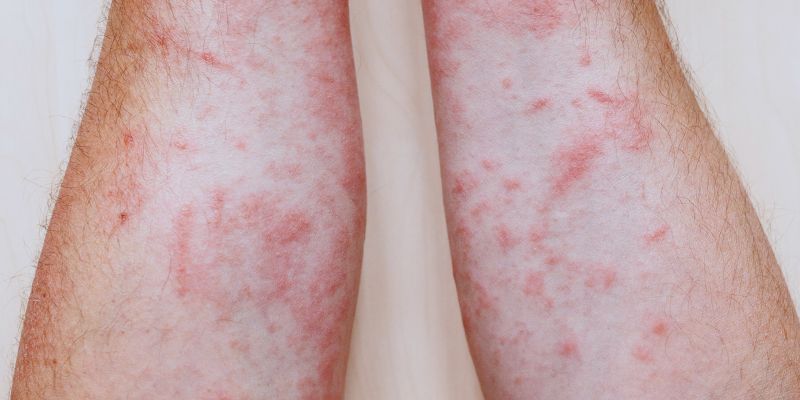
Different skin rashes from dermatomyositis usually appear on the elbows, knuckles, and face. Sunlight aggravates these rashes, which may be red or purple. Persistent skin inflammation causes itching, irritation, and pain. Patients might start to have scars and skin thickening over time. Sometimes, painful ulcers develop, raising the risk of infections. Moversives and topical corticosteroids help lower symptoms and prevent problems.
Protection of delicate skin from additional injury depends on sunscreen. Some people need oral medicines to lower inflammation. Check-ups in dermatology assist in monitoring long-term skin conditions. Good skin care stops the aggravation of symptoms. Skin problems could last even after muscular symptoms go away. A mild skincare regimen will help patients avoid discomfort. Control of skin problems enhances general comfort and quality of life.
Calcinosis: Calcium Deposits in Soft Tissues
Calcium deposits forming in the skin, muscles, and joints cause a condition known as calcinosis. In long-term dermatomyositis instances, this disorder is rather common. Deposits hinder mobility and create edema and pain. They could break through the skin and cause infections. Though the precise origin of calcinosis is uncertain, persistent inflammation is involved. Furthermore, inadequate calcium metabolism could influence its growth. These deposits are found by X-rays and CT scans.
Physical therapy and pain management help symptoms disappear. Some individuals need surgery for big calcium deposits. Bisphosphonates are a medication that slows down progression. A balanced diet helps muscles and bones remain strong. Stopping chronic inflammation lowers the chance of calcinosis. If discomfort worsens, patients should monitor symptoms and consult a doctor. Controlling calcium deposits increases comfort and mobility.
Infections Due to Weakened Immune System
Dermatomyositis compromises the immune system, so infections are more common. Patients run more chances of urinary tract infections, skin infections, and respiratory problems. Treatments, including steroids, further reduce immune system activity. Infections by bacteria and viruses can aggravate dermatomyositis symptoms. Serious concerns are pneumonia and bloodstream infections. Vaccinations guard against pneumonia and the flu. It is important to maintain proper hygiene and avoid sick people.
If infections arise, doctors might prescribe antibiotics or antiviral medicines. Frequent blood tests track immune system response. Patients should immediately report fever, chills, or ongoing coughing. Stopping infections enhances long-term health results—strong immune systems aid in lowering problems and flare-ups. Good medical treatment lowers the hazards connected to a compromised immune system.
Conclusion:
Dermatomyositis compromises internal organs, skin, and muscles. It causes coughing, cardiac issues, lung disease, and trouble swallowing. Other patients get cancer, infections, or calcium deposits. Early control lessens major issues. Changes in lifestyle, medical treatments, and mental health assistance can help to raise the quality of living. Frequent visits help to avoid long-term damage. For improved disease control, patients should do as advised by their doctor. Knowing the consequences of dermatomyositis enables early treatment. Good general health and comfort depend on timely care. Better long-term results depend on continuous medical assistance.